Orthopedic decision-making depends on accurate representation of anatomy—particularly when joint alignment and bone relationships change…

pedCAT Shown to be Most Effective Imaging Option for Mülller-Weiss Disease
The CurveBeam pedCAT imaging system was recently recommended as an incredibly beneficial option for the treatment and analysis of Mülller-Weiss disease. While the disease can be detected in its early stages with magnetic resonance imaging and radiographs, there is a considerable advantage to using weight-bearing computed tomography (WBCT) for diagnosis and evaluation.
Mülller-Weiss involves a painful deformity caused by osteonecrosis and fragmentation of the navicular, most commonly occurring in adults and disproportionately in female patients. The pedCAT, a cone beam CT imaging system, provides an opportunity for early diagnosis and better preoperative analysis, resulting in improved treatment. Standard computed tomography (CT) in itself beneficial for several reasons.
and fragmentation of the navicular, most commonly occurring in adults and disproportionately in female patients. The pedCAT, a cone beam CT imaging system, provides an opportunity for early diagnosis and better preoperative analysis, resulting in improved treatment. Standard computed tomography (CT) in itself beneficial for several reasons.
First, it allows for easier examination of the extent of the deformity and for evaluation of any surrounding arthritis. With CT data, surgeons can evaluate and plan for any future attempts at remedying the deformity.
However, because standard CT scans are not weight bearing, they do not provide an accurate view of the relationship between the hindfoot and midfoot deformity. pedCAT WBCT scans allow doctors to go one step further than standard CT scans.
pedCAT 3D datasets can be fully manipulated in order to provide an opportunity for in-depth analysis before proceeding with surgery on a complex deformity. In addition, the pedCAT provides for a better patient experience as the procedure only takes between 19 and 48 seconds, depending on the extent of the deformity.
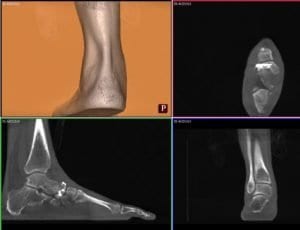
The pedCAT also cuts down on radiation, with a low dose of 1.4 μSv, an amount that is not significantly higher than the 0.7 μSv dosage of the traditional three radiographs of a foot taken to identify Mülller-Weiss. Overall. the pedCAT allows for an accurate and thorough analysis that cannot be achieved through normal X-rays, MRIs nor bone scans.
When creating a treatment plan for Mülller-Weiss disease, the goal is to reestablish a balanced foot, which may require realignment surgery or surgery involving a structural graft.
Due to the complexity inherent in any attempt at treatment, pedCAT imaging is ideal, as it allows doctors to accurately gauge the amount of medial column shortening as well as determine the navicular bone stock and density.
Identifying these key details as accurately as possible is imperative for operations such as calcaneal osteotomy to properly restore alignment or repairing the medial column length.
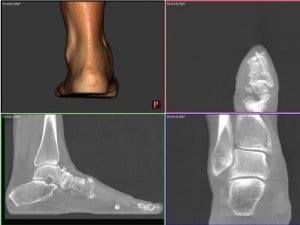
While a combination of weight bearing X-Ray and unloaded CT scanning are sometimes suggested as an alternative, the degree of the deformity caused by Mülller-Weiss will not be accurately represented.
It is only through WBCT scanning that a true picture of the dynamics within the foot will be understood. pedCAT is a compact and ultra low-dose system, which aims to make such 3D scanning possible for clinics.




